Hitachi Virtual Storage Platform(VSP) Architecture
Hitachi Virtual Storage Platform (VSP) Architecture
The Hitachi VSP architecture is a modular based enterprise-level storage system.
A fully configured VSP will contain a maximum of 6 racks with 2 DKC units and 16 DKU units. It can be configured as a single chassis or dual chassis. Each chassis has at least one DKC and one or two DKUs (DKC and DKU are explained later in this post). An illustrated diagram of a fully configured VSP is shown below.
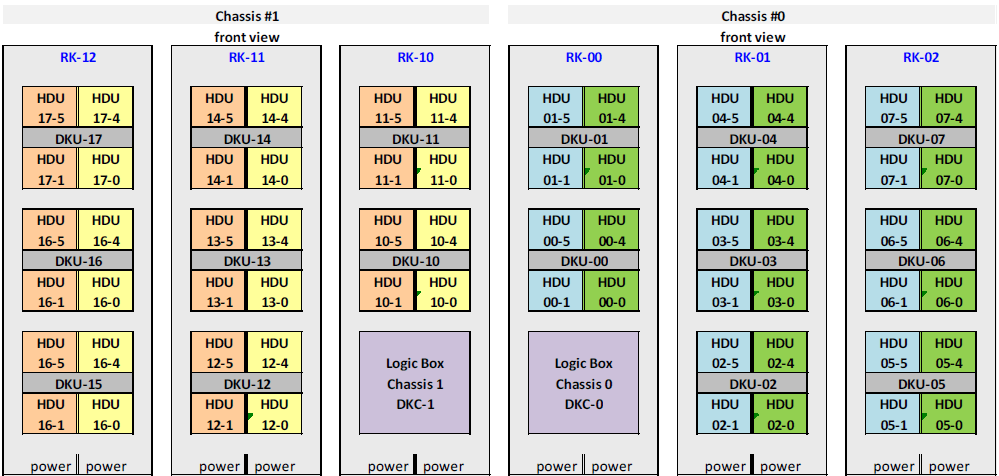 Hitachi Virtual Storage Platform(VSP) Architecture
Hitachi Virtual Storage Platform(VSP) Architecture
The main components in VSP are disk controller (DKC) and disk unit (DKU).
Disk controller (DKC) is the heart of VSP. All operations in VSP are handled by DKC.
Disk unit (DKU) is a collection of physical hard drives.
Two DKCs are interconnected via grid switches (GSW).
The main components in DKC are
- Frontend directors (FED)
- Backend directors (BED)
- Virtual storage directors (VSD)
- Cache adapters
- Service processor
- Grid Switch
- Power supplies, cooling fans, etc.
and DKU contains
- Hard drives
- SAS switch
- Cooling fans
- Power supplies
Details description of the components is here
Below diagrams display the front and back sides of DKC


DKC design is modular based and most of the components are replaceable units. Virtual directors and cache directors are placed on the front side of DKC. FEB, BED, service processor, and grid switches/express switches are placed on the back side of DKC.
Each LDEV is assigned one VSD (virtual storage director) to process I/Os. Each LDEV is owned by one VSD at a time. This LDEV ownership is passes temporarily if the VSD board fails.
Architecture of VSP
The basic system architecture of VSP is

In VSP FEDs, BEDs, cache directors (CMA), and Virtual storage directors are communicated through Grid switches (GSW). All director components are directly connected to Grid switches that form the Histar-E network.
Channel adapters (FEDs) are for Host connectivity and Disk adapters (BEDs) are for backend disk connectivity.
VSDs are I/O processing boards and are responsible for processing I/O from FEDs to BEDs.
Whenever a host sends an I/O request, FED receives the request and communicates with VSD. VSD processes requests and sends the information to the cache and BEDs. If requested data is available in the cache it directly responds with data. If requested data is available in the cache it fetches the data from Backend disks and serves the data.
Spare drives
VSP has spare drives in case of any hard drive failure. It supports dynamic sparing. It means if a hard drive is suspected to fail or gets I/O errors more than a threshold value, the Storage system starts copying data to the spare drive even if it has not failed.
In this case, data copied to the spare drive is not recreated. It is a pre-emptive copy.
If the drive failed and a pre-emptive copy does not exist. The spare drive becomes part of that RAID group and starts rebuilding data by using parity. It is called a correction copy.
Hi-Track Monitor:
It is software that is installed on the Service processor (SVP). It keeps monitoring VSP at all times. Collects the hardware status and error data. It sends collected data to Hitachi Data Systems(HDS) support center for analysis. If any hardware occurs Hi-Track monitor immediately reports to the service center.
Hi-Track monitor enables the HDS support team to access VSP remotely as they were at the site.
Hi-Track SVP agent is a tool installed on the Service processor (VSP). It performs error monitoring and sends email alerts to customers.